We have already covered why you should write a Business plan and what should be the content of it. When establishing your business it is key to build the base by defining what you are offering, how your are offering it, whom you are offering it to, and how you plan to generate revenue. This can be a challenging task due to its vast amount of information to process.
That’s where the Business Model Canvas comes in. The Business Model Canvas is a management tool proposed by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur whichs purpose is exactly what the name states – it’s your one-page roadmap to developing, analyzing, and refining your business model.
The Canvas offers you a template divided into the following areas:
- Key Partners
- Key Activities
- Key Resources
- Value Propositions
- Customer Relationships
- Channels
- Customer Segments
- Cost Structure
- Revenue Streams
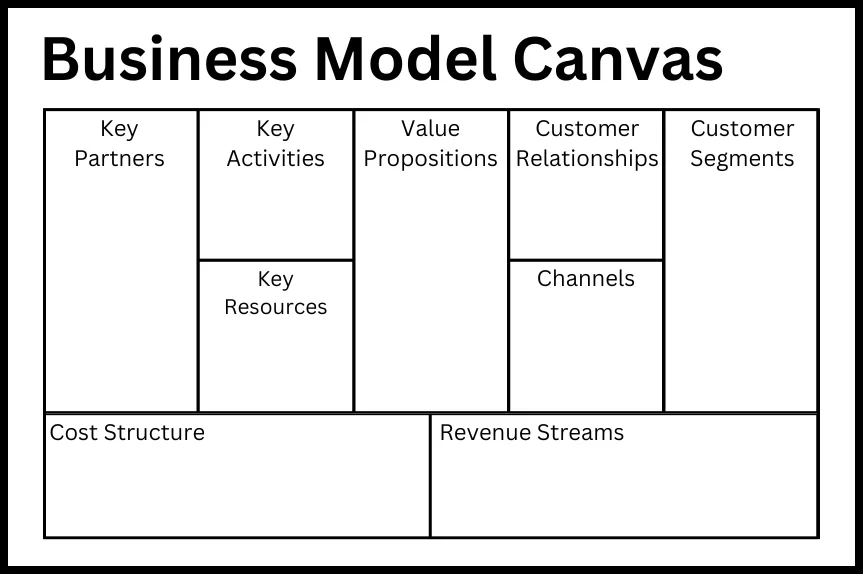
The Following descriptions for those areas shall support you with designing the Business Model. Also if you like having your Business Model written down in good old paper, I have created a book (Business Model Canvas Helper) which contains the mentioned following descriptions and gives you the space to write down your Business Idea.
Key partners
Definition:
Describes the network of suppliers and partners that make the business model work.
Identify who your key partners are and how they will help you achieve your business goals. Understand the importance of partnerships in creating value and reducing risks.
Questions to Ask:
- Who are our Key Partners?
- Who are our Key Suppliers?
- Which Key Resources are we acquiring from partners?
- Which Key Activities do partners perform?
Key partners are the external companies or suppliers that will help you carry out your Key Activities. These partnerships are forged in order to reduce risks and acquire resources.
Types of partnerships are
- Strategic alliance: partnership between non-competitors
- Coopetition: strategic partnership between partners
- Joint ventures: partners developing a new business
- Buyer-supplier relationships: ensure reliable supplies
Key Activities
Definition:
Describes the most important things a company must do to make its business model work.
Define the essential activities your business must undertake to succeed. Learn to identify the most crucial tasks that will drive your business forward.
Questions to Ask:
- What Key Activities do our Value Propositions require?
- Our Distribution Channels?
- Customer Relationships?
- Revenue Streams?
In this section, you should list down all the key activities you need to do to make your business model work.
There are 3 categories of key activities;
- Production: designing, manufacturing and delivering a product.
- Problem-solving: finding new solutions to individual problems.
- Platform/Network: Creating and maintaining platforms.
Key Resources
Definition:
Describes the most important assets required to make a business model work.
Discover the key resources needed for your business operations. Understand what assets are vital for delivering your value proposition, reaching your customers, and sustaining your operations.
Questions to Ask:
- What Key Resources do our Value Propositions require?
- Our Distribution Channels?
- Customer Relationships?
- Revenue Streams?
This is where you list down which key resources or the main inputs you need to carry out your key activities in order to create your value proposition.
There are several types of key resources and they are
- Human (employees)
- Financial (cash, lines of credit, etc.)
- Intellectual (brand, patents, IP, copyright)
- Physical (equipment, inventory, buildings)
Value Proposition
Definition:
Describes the bundle of products and services that create value for a specific Customer Segment.
Craft compelling value propositions that address your customers' needs and set you apart from the competition. Learn to articulate what makes your business unique and desirable.
Questions to Ask:
- What value do we deliver to the customer?
- Which one of our customer’s problems are we helping to solve?
- What bundles of products and services are we offering to each Customer Segment?
This is the building block that is at the heart of the business model canvas. And it represents your unique solution (product or service) for a problem faced by a customer segment, or that creates value for the customer segment.
If you are offering a new product, it should be innovative and disruptive. And if you are offering a product that already exists in the market, it should stand out with new features and attributes.
Customer Relationships
Definition:
Describes the types of relationships a company establishes with specific Customer Segments.
Develop strategies for building and maintaining strong customer relationships. Understand the different types of relationships you can establish and how they contribute to your business's success.
Questions to Ask:
- What type of relationship does each of our Customer Segments expect us to establish and maintain with them?
- Which ones have we established?
- How are they integrated with the rest of our business model?
- How costly are they?
In this section, you need to establish the type of relationship with your customer segments or how you will interact with them.
There are several types of customer relationships
- Personal assistance
- Dedicated personal assistance
- Self-service
- Automated services
- Communities
- Co-creation
Channels
Definition:
Describes how a company communicates with and reaches its Customer Segments to deliver a Value Proposition.
Identify the most effective channels to reach your customers and deliver your value proposition. Learn how to integrate and optimize your distribution channels.
Questions to Ask:
- Through which channels do our customer segments want to be reached?
- How are we reaching them now?
- How are our Channels integrated?
- Which ones work best?
- Which ones are most cost-efficient?
This block is to describe how your company will communicate with and reach out to your customers. Channels are the touchpoints that let your customers connect with your company.
Channels play a role in raising awareness of your product or service among customers and delivering your value propositions to them.
There are two types of channels
- Owned channels: company website, social media sites, in-house sales, etc.
- Partner channels: partner-owned websites, wholesale distribution, retail, etc.
Customer Segments
Definition:
Defines the different groups of people or organizations an enterprise aims to reach and serve.
Segment your customer base to better understand their needs and tailor your offerings. Learn the importance of targeting the right audience for your products or services.
Questions to Ask:
- For whom are we creating value?
- Who are our most important customers?
- What are the customer archetypes?
There are different customer segments a business model can target and they are:
- Mass market
- Niche market
- Segmented
- Diversified
- Multi-sided markets
Cost Structure
Definition:
Describes all costs incurred to operate a business model.
Analyze your cost structure to ensure your business is financially viable. Understand the key costs associated with your business model and how to manage them effectively.
Questions to Ask:
- What are the most important costs inherent in our business model?
- Which Key Resources are most expensive?
- Which Key Activities are most expensive?
In this block, you identify all the costs associated with operating your business model.
You’ll need to focus on evaluating the cost of creating and delivering your value propositions, creating revenue streams, and maintaining customer relationships.
And this will be easier to do so once you have defined your key resources, activities, and partners.
Revenue Streams
Definition:
Represents the cash a company generates from each Customer Segment (costs must be subtracted from revenues to create earnings).
Explore various revenue streams to determine how your business will make money. Learn to identify and optimize different ways to generate income.
Questions to Ask:
- For what value are our customers really willing to pay?
- How are they currently paying?
- How would they prefer to pay?
- How much does each Revenue Stream contribute to overall revenues?
Revenues streams are the sources from which a company generates money.
A revenue stream can belong to one of the following revenue models:
- Transaction-based revenue
- Recurring revenue
There are several ways you can generate revenue from
- Asset sales
- Usage fee
- Subscription fee
- Lending/ leasing/ renting
- Licensing
- Brokerage fees
- Advertising
Conclusion
Creating a solid Business Model can feel like a daunting task. But by breaking it down into bite-sized pieces with the Business Model Canvas, you make the process manageable and structured. Start by brainstorming your ideas, then use the Canvas to map out each part of your business model, from your value proposition to your revenue streams.
Remember, every great business starts with a clear plan!
Here are some examples for a Business Model Canvas
Here is a enhanced Business Model Canvas Template for you to download:




